- Home
- >
- Knowledge Center
- >
- Blogs
Blogs
Sharing knowledge is key to an innovative and healthy industry! This knowledge center is therefore a central place on our website to share information. Read all about our industry in the blogs below!
Understanding Die Casting Molds and Their Applications?
Die Casting Molds play a crucial role in the manufacturing industry. These molds shape metals into precise forms, contributing significantly to various sectors. According to a report from MarketsandMarkets, the global die casting market is projected to reach $80.9 billion by 2026, growing steadily. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for lightweight and durable components in automotive and aerospace applications.
An expert in this field, Dr. John Smith, emphasizes, "The efficiency of Die Casting Molds directly impacts production quality and cost." His insight underscores the importance of selecting the right mold. Choosing the wrong design can lead to defects and wasted resources. Industries often overlook the need for regular mold maintenance, which can be detrimental.
Die Casting Molds are not just tools; they are vital components that influence the entire production process. Understanding their design and application can enhance efficiency. Regular assessments and upgrades of these molds are necessary for maintaining quality. Despite their importance, many companies continue to face challenges in optimizing mold performance. Investing in education and technology is essential for improvement.
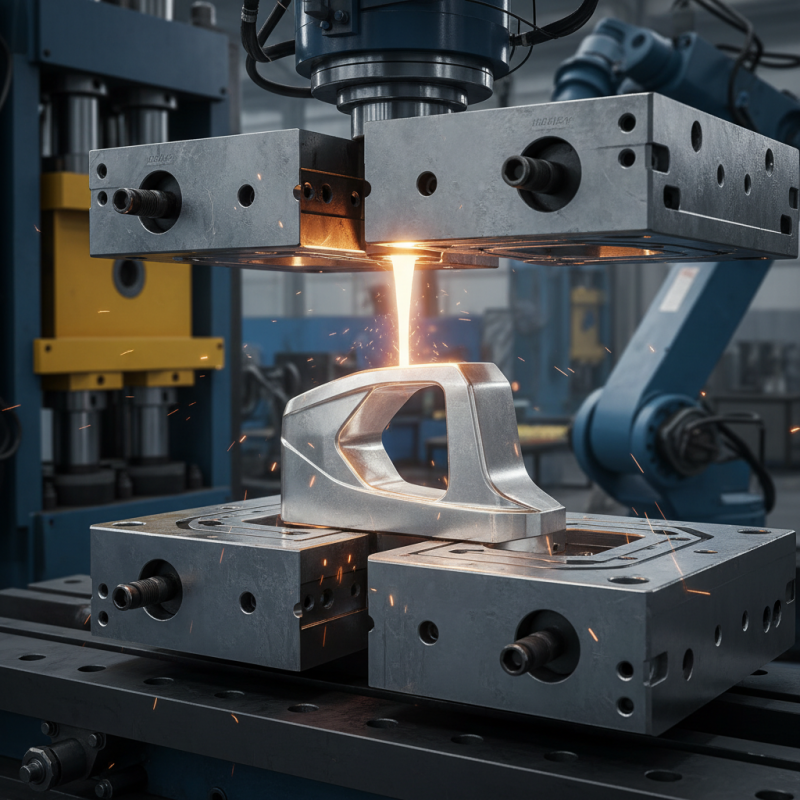
Overview of Die Casting Molds and Their Functionality
Die casting molds play a crucial role in the manufacturing process. They are designed to create specific shapes and sizes in metal parts. The molds are made from strong materials, facilitating repeated use. Each mold is engineered to withstand high pressure and temperatures. This results in a high level of detail and precision in the finished product.
In die casting, liquid metal is poured into these molds. Once cooled, the molds are opened, revealing the final shape. However, it is essential to ensure the mold does not have defects. Imperfections can lead to flaws in the final product. Quality control measures are necessary to prevent this.
The applications of die casting molds are diverse. Industries utilize them to produce automotive components, household items, and electronics. Each application demands unique mold designs and functionalities. Nonetheless, the need for innovation and improvement is constant. A mold that works well today may need adjustments tomorrow. Continuous learning is vital in mold design and manufacturing.
Understanding Die Casting Molds and Their Applications
| Mold Type | Material | Temperature Resistance (°C) | Applications | Lifespan (Shots) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Pressure Die Casting | Aluminum Alloy | 600 | Automotive Parts, Appliances | 100,000 |
| Gravity Die Casting | Zinc Alloy | 400 | Electronics, Hardware | 50,000 |
| Low Pressure Die Casting | Magnesium Alloy | 300 | Aerospace Components | 80,000 |
| Die Casting with Inserts | Tin Alloy | 350 | Medical Devices | 60,000 |
Types of Die Casting Molds: Permanent vs. Temporary Molds
Die casting molds play a critical role in manufacturing. They are used to shape molten metal into precise forms. There are two primary types of die casting molds: permanent and temporary. Each serves a unique purpose, influencing production methods and costs.
Permanent molds are made from metal. They are durable and can be reused many times. This makes them ideal for high-volume production. The design process can be complex. It requires precise calculations to ensure consistency. On the downside, the initial costs for permanent molds can be high. It may not be cost-effective for low production runs.
Temporary molds, such as sand or plaster molds, offer flexibility. They are easier and quicker to create. This makes them suitable for prototype development or smaller batches. However, their lifespan is limited. They may not withstand high pressures or temperatures as well as permanent molds. This can lead to inconsistencies in the final product. Choosing between these molds requires careful consideration of the project's needs and budget.
Materials Used in Die Casting Molds and Their Properties
Die casting molds are crucial in manufacturing. They are made from various materials, each with unique properties. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and copper alloys. Steel molds are durable and can withstand high temperatures. They are suitable for large production runs. However, they can be expensive and heavy.
Aluminum molds, on the other hand, are lightweight and offer shorter lead times. They are less durable than steel but can be ideal for smaller runs. Copper alloys provide excellent thermal conductivity, which can enhance the cooling process during casting. However, they are generally more costly and can corrode more quickly.
Tips: Choose the right material based on your production needs. Do not overlook the importance of thermal properties in your mold selection. Reflect on the cost versus durability trade-offs. It's essential to find a balance for your specific applications. Remember, the wrong choice can lead to higher long-term costs.
Materials Used in Die Casting Molds and Their Properties
Applications of Die Casting Molds in Various Industries
Die casting molds play a crucial role in manufacturing processes across various industries. These molds are used to create intricate shapes with precision, making them invaluable in sectors like automotive, aerospace, and electronics. For instance, the automotive industry relies on die casting to produce lightweight and durable components. This can lead to improved fuel efficiency and performance in vehicles.
In electronics, die casting molds help create housings and heat sinks. These components are essential for the longevity and reliability of electronic devices. The ability to create complex geometries helps companies reduce assembly time and costs. Yet, the design of these molds can be a challenge. The slightest error can lead to defects, wasting time and resources.
**Tip:** Always involve engineers early in the mold design process. Their expertise can streamline production and minimize errors.
A common mistake is overlooking the cooling channels in the mold design. Inefficient cooling can cause warping or surface defects. It’s vital to invest time in designing proper cooling systems.
**Tip:** Conduct thorough simulations before finalizing mold designs. This can help identify potential challenges ahead of production.
Maintenance and Care for Optimal Performance of Die Casting Molds
Die casting molds require regular maintenance for optimal performance. Keeping them clean is crucial. Debris can cause defects in production. Inspect molds frequently for wear and tear. Minor issues can escalate if ignored.
Tips for maintenance: Always clean molds with a soft cloth. Avoid harsh chemicals that can damage the surface. Lubrication is key to reducing friction. Ensure that you use the right type of lubricant for your molds.
Monitor temperature during the die casting process. Excessive heat can warp molds, leading to poor-quality products. Look out for signs of thermal fatigue. Regular checks can help you catch problems early. This is an area that often gets overlooked.
Mold degradation can occur unexpectedly. It often happens with high-volume production. Keep records of mold usage and performance. This can guide necessary adjustments and replacements. It is an ongoing process and requires diligence.
